go语言实现sqrt的方法(重写Quake III卡马克快开平方根)
在3D图形编程中,经常要求平方根或平方根的倒数,例如:求向量的长度或将向量归一化。C数学函数库中的具有理想的精度,但对于3D游戏程式来说速度太慢。我们希望能够在保证足够的精度的同时,进一步提高速度。
根据John Carmack在Quake III源代码中SquareRootFloat,该功能可以计算浮点数的平方根的倒数,比常规的
float SquareRootFloat(float number) {
long i;
float x, y;
const float f = 1.5F;
x = number * 0.5F;
y = number;
i = * ( long * ) &y;
i = 0x5f3759df - ( i >> 1 );
y = * ( float * ) &i;
y = y * ( f - ( x * y * y ) );
y = y * ( f - ( x * y * y ) );
return number * y;
}
由专家数学家(Chris Lomont)开发的一个稍好一点的常数,该常数试图找出原始算法的工作原理:
float InvSqrt(float c)
{
float xhalf = 0.5f * x;
int i = * (int *) &x;
i = 0x5f3759df - (i >> 1);
x = * (float *) &i;
x = x * (1.5f - xhalf * x * x);
return x;
}
func InvSqrt(x float32) float32 {
var xhalf float32 = 0.5 * x // get bits for floating VALUE
i := math.Float32bits(x) // gives initial guess y0
i = 0x5f375a86 - (i >> 1) // convert bits BACK to float
x = math.Float32frombits(i) // Newton step, repeating increases accuracy
x = x * (1.5 - xhalf*x*x)
x = x * (1.5 - xhalf*x*x)
x = x * (1.5 - xhalf*x*x)
return 1 / x
}
math.Float32bits 底层使用了unsafe.pointer,进一步改写后变成
func InvSqrt(x float32) float32 {
var xhalf float32 = 0.5 * x // get bits for floating VALUE
i := *(*uint32)(unsafe.Pointer(&x)) // gives initial guess y0
i = 0x5f375a86 - (i >> 1) // convert bits BACK to float
x = *(*float32)(unsafe.Pointer(&i)) // Newton step, repeating increases accuracy
x = x * (1.5 - xhalf*x*x)
x = x * (1.5 - xhalf*x*x)
x = x * (1.5 - xhalf*x*x)
return 1 / x
}
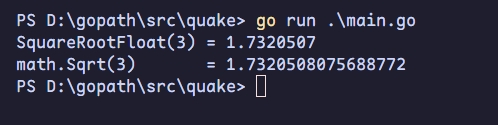
最后运行3的平方根倒数得到的结果与go自带math.sqrt结果做对比

发表评论: